Wi-Fi Evolution Understanding the Advancements of IEEE 802.11 Standards
IEEE 802.11 is a set of standards developed by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) for wireless local area networks (WLANs). It is commonly referred to as Wi-Fi, which stands for wireless fidelity.
The first version of the standard, 802.11, was released in 1997 and provided a maximum data rate of 2 Mbps. Since then, several updates and improvements have been made, including the addition of higher data rates, improved security, and support for more devices.
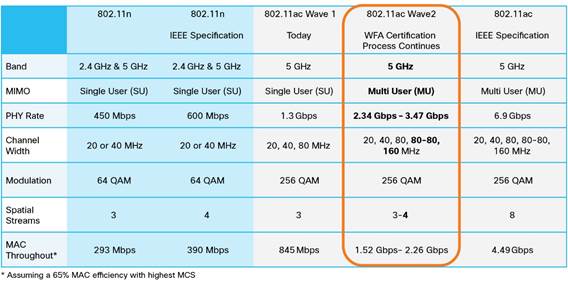
The latest iteration of the standard, 802.11ax, touted as Wi-Fi 6, boasts faster speeds, enhanced capacity, and superior performance in crowded settings in comparison to its predecessors. It also has improved power efficiency, which is beneficial for devices with limited battery life, such as smartphones and laptops.
IEEE 802.11 technology is widely used in homes, businesses, and public places to provide wireless internet access. It is supported by a wide range of devices, including smartphones, laptops, tablets, and smart home devices.
In summary, IEEE 802.11 is a set of standards for wireless local area networks (WLANs) commonly known as Wi-Fi. It has undergone several updates and improvements, with the latest version being 802.11ax (Wi-Fi 6) which offers faster speeds, improved capacity, and power efficiency. It is widely used in homes, businesses, and public places to provide wireless internet access and is supported by a wide range of devices.
Here are some data rates and frequencies for different versions of IEEE 802.11:
- IEEE 802.11a: Uses the 5 GHz frequency band and provides data rates up to 54 Mbps.
- IEEE 802.11b: Uses the 2.4 GHz frequency band and provides data rates up to 11 Mbps.
- IEEE 802.11g: Uses the 2.4 GHz frequency band and provides data rates up to 54 Mbps.
- IEEE 802.11n: Uses both the 2.4 and 5 GHz frequency bands and provides data rates up to 600 Mbps.
- IEEE 802.11ac: Uses the 5 GHz frequency band and provides data rates up to 1 Gbps.
- IEEE 802.11ax: Uses both the 2.4 and 5 GHz frequency bands and provides data rates up to 9.6 Gbps.
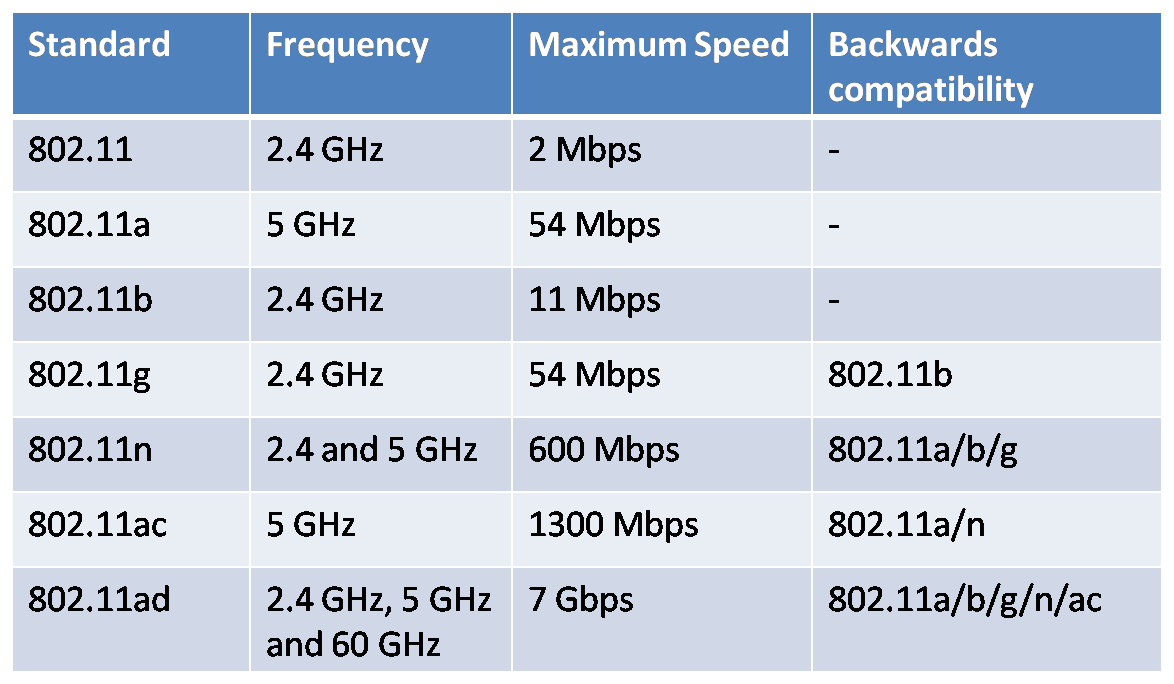
It’s worth mentioning that the actual data rates achieved in real-world scenarios may be lower than the theoretical maximums due to various factors such as interference, distance, and the number of devices connected to the network.
Also, the latest version of IEEE 802.11 is 802.11be which is in the development stage and it is targeting to provide a 12 Gbps data rate.
