The Rise of Humanoid Robots: Hype or Reality?

What Are Humanoid Robots
The humanoid robots are robots that are built in the form and that of humans and are usually constructed with a torso, a head, two arms, and two legs. Their design does not just stop at their appearance, they can move and behave like human beings with abilities like walking, holding things, and communicating with objects and human made environments. Humanoid robots are mobile and flexible unlike other robots which are usually designed to perform a particular task and work in stationary locations and can be used in dynamic conditions where humanoid robots can use human tools and navigate their human habits.
They are distinguished by the form and locomotion that are human-like as compared to other forms of robots. The majority of other robots will be specially-shaped and restricted in their mobility, which is intended to perform a specific task, such as an industrial robotic arm or a transport robot on a wheel. Humanoids and related robots often possess legged locomotion to simulate human locomotion and balance to carry out activities that require interaction in human-centric environments, e.g. climbing stairs or using human tools.
Examples of humanoid robots currently in existence are:
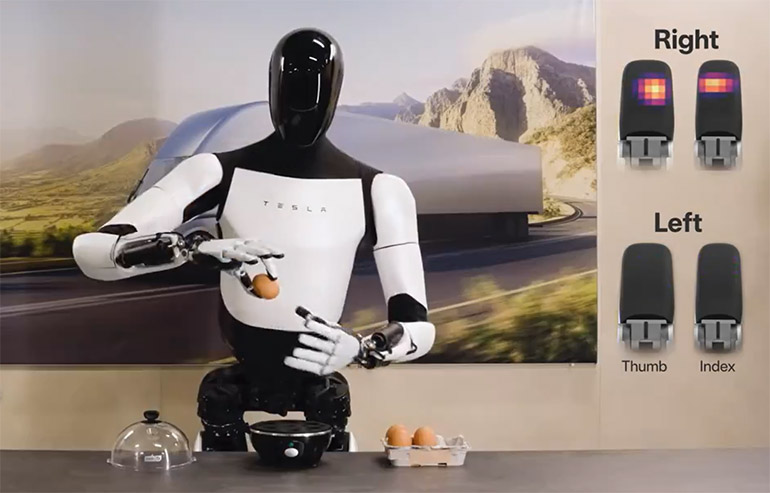
Tesla Optimus: This model is intended to perform factory chores and logistic operations and has AI that is modified after Tesla self-driving technology. It is independent in navigation through factories, handling of objects and even acquiring new skills through observation.

Honda Asimo: An innovative humanoid robot that is able to walk, run, and interrelate with human beings in service functions.
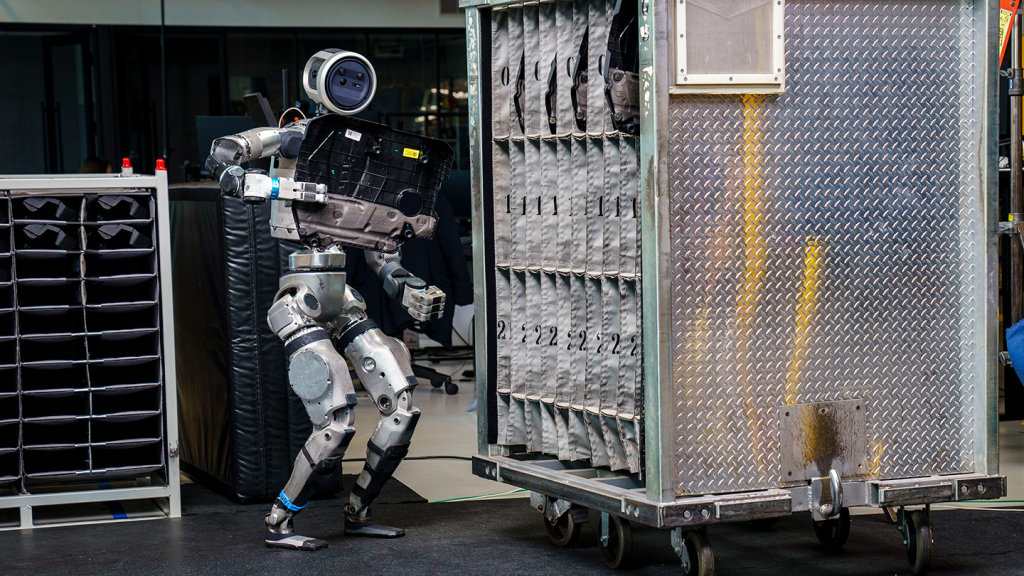
Boston’s Dynamics: Atlas: A very agile robot that is featured with dynamic movements such as running, jumping and parkour; this is primarily a research platform to enhance humanoid agility and control of the robotics.

The Technology behind Humanoid robots.
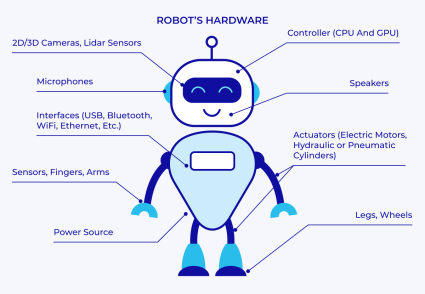
Humanoid robots combine sophisticated technologies in the area of AI and machine learning, computer vision, and robotics hardware in order to act and communicate intelligently. AI allows them to experience environments, comprehend instructions, decide and gain experience. Machine learning, in particular, reinforcement learning, assists them in acquiring self-directed behaviors through trial and error. Computer vision is the visual vision of cameras and sensors, which enables the robot to identify objects, navigate, and communicate with the human and tools. Actuators to simulate muscle movements and sensors to give position, force and balance information are part of robotics hardware and coordinate complex movements in real time.
Cameras, gyroscopes, tactile sensors, force sensors and other sensors sense the environmental and robot states. The control signals are converted into fined tuned mechanical response such as walking, grasping or balancing by actuators such as motors and hydraulic systems. Motion control systems rely on algorithms in movement coordination that allow the system to react dynamically to sensor data to ensure stability, adapt to terrain and fine motor control tasks. Neural networks especially deep learning are real-time processors and optimize control of the motor and perception based on the data streams of huge sensors.
Big Language Models (LLMs) are important high-level planners and communicators in the humanoid robots. They process natural language commands, convert them into action plans and coordinate the low-level controllers. The flexibility of LLMs is achieved through their ability to comprehend and perform multi-step instructions that require complex instructions and are able to engage with humans in a natural way. These models have the ability to reason, solve problems and offer contextual awareness to the decision-making process, and serve as the brain of the robot in intelligent behavior planning.
Current Applications of Humanoid Robots
The humanoid robots are beneficial in manufacturing and logistics since they can be used to carry out repetitive or physically challenging tasks with a high level of accuracy. In the factories, they are able to assemble, conduct quality checks, or deal with hazardous materials that are dangerous to humans. Their dexterity of the human nature enables them to utilize typical tools and move objects made to be used by humans. Humanoid robots can be used in warehouses to deliver materials, pack packages, and manage inventory. They are also flexible to work with human employees without any danger of losing productivity and causing fatigue.
Humanoid robots have been used as interactive teaching tools and as experimental platforms in education and research to develop AI and robotics itself. They can be used in STEM learning to create the desire and interest in robotics, coding, and engineering, by giving students of different ages a hands-on experience. Due to the ability to imitate human speech, expressions, and movements, humanoid robots make it easier to engage and learn in such disciplines as language, communication, and social robotics. These robots are used by the researchers as testbeds of designing advanced perception and decision-making and human-robot interaction algorithms. The fact that the robots can learn and develop can investigate new horizons of AI such as emotional recognition and independent behavior.
Lastly, the humanoid robots have significant application in disaster response and exploration where humans are exposed to or cannot be exposed to dangerous conditions. Such robots can work in dangerous areas like earthquake zones or nuclear disaster areas to conduct searches and deliver supplies or analyze the damage. Their anthropomorphic shape helps them to cross trash-infested areas and use human equipment. Humanoid robots will help to solve maintenance issues or carry out experiments on their own in space missions, making missions possible and without risking human life. Humanoid robots with sensors and movement are also valuable underwater exploration to survey the ecosystem or repair infrastructure.
The Future Potential
The future of humanoid robotics is in the possibility of the expansion of uses of the robot as the multifunctional helper in daily life, space missions, and the working process with people.
Humanoid robots will be used in real-life support, and it is anticipated that they will become personal assistants in homes, helping with everyday tasks, taking care of elderly and disabled people, and controlling intelligent homes. Their incorporation into smart city infrastructure may enable them to offer benefits to the people like security patrols, information kiosks, and maintenance services to improve the city life and accessibility.
Humanoid robots will be important in the long-duration missions to the Moon, Mars, or other galaxies since they will support the astronauts. They are able to carry out normal maintenance work, check equipment and help with scientific experiments under extreme conditions which make human members of the crew vulnerable. Their capability to evolve and work autonomously will be highly important to deep-space missions where communication delays prevent real-time control.
Humanoid robots are also very promising in working collaboratively in other areas such as construction and agriculture where they can work side by side with people in engaging in heavy work, precision work or even repetitive work, where they make work safer and efficient. Robots may also become partners in the creative sector like design, art, and entertainment, providing new tools or concepts that can be used by human creativity.
In general, the future of humanoid robots is inclined to more combined functions which will be enriching the human capabilities in various environments and thus making life safer, more efficient and more innovative.
Hype vs. Reality
Some of the practical uses of humanoid robots today include logistics, healthcare assistance, retail, maintenance of the public places, elderly care, and last-mile deliveries. They supplement human services, enhance safety in the workforce and resolve labor shortages particularly in aged communities. Nevertheless, genuine general intelligence, profound emotional awareness, and human-like skill is still something that exists only in the science fiction. The market trends are heavily growing with large corporations such as Tesla, Boston Dynamics, and Agility Robotics being innovative with a solid investment and a national strategy drive, notably in the United States and China.
Humanoid roles that exist in practice to-day.
- Humanoid robots are used in logistics (e.g., the huge amounts of robots that Amazon implements), health care assistance, geriatrics, retail service, and street maintenance. They work on hazardous or repetitive tasks that demand precision, and more importantly allow the human workers to engage in more rewarding tasks.
- The development of humanoid robots is being tested by the companies in complex, real-world applications like last-mile delivery with human workers, which exemplifies the shifting abilities of the robots.
- Advanced sensor integration, AI perception, autonomous decisions, and powerful motion control allow them to be versatile, but physical dexterity remains low relative to humans.
Still Elements of Science Fiction.
- It is not yet within the capabilities of the current technology to provide true general intelligence such that robots can be able to learn and adapt to any human-context problem independently.
- Great emotional insight, or empathetic feeling and reaction between the robot and the emotion of a man, is mostly theoretical at this point.
- There is also human-like dexterity; this fineness of manipulation using human hands with its sensitivity, speed, and adaptability is still technically difficult and not yet achievable.
Trends and Major Market participants.
- Humanoid robot will hit a market size of more than 180 billion by 2035, compared to 7.8 billion in 2025 with a healthy CAGR of 37.
- The old-school industrial robotics companies have stayed on top, but now with growing competition against AI-based startups and technology giants.
- One of the biggest competitors is Tesla whose Optimus humanoid robot would be a huge component of Tesla valuation. Elon Musk envisages that humanoids will add significantly to the future value of Tesla.
- Boston Dynamics is also developing agile and dynamic humanoids and Agility Robotics is also making ground in delivery and logistic robots.
- These firms, as well as other firms such as Figure AI and Unitree, are driving commercialization and strategic development.
- The robotics industry in the U.S. is lobbying to have a national strategy in order to stay ahead of its rivals such as China, which has proclaimed humanoid robotics a national priority.
In brief, the current humanoid robots are useful in industrial and service applications, but are not yet endowed with higher levels of human-like intelligence or emotions. The market continues to grow fast with good momentum propelled by major companies and government efforts pushing the envelop of what these robots are capable of doing.
