The Impact and Evolution of 5G: Technology, Safety and the future of smart innovation

Introduction
The dynamics of mobile communication technology has enhanced the velocity at which the world has transformed in terms of connectivity, interactions and even digital world experience. Ever since the primitive days of the analog voice communications in 1G and the introduction of the faster internet in 4G, wireless networks have increasingly kept pushing the boundaries. With advent of 5 G technology, there is a fresh start, and it is far more than the faster internet connectivity on the smartphone.
5G is not sleeker 4G but a makeover in the mobile network architecture to meet the insatiable future needs. Because of its lightning-speed data transmission and a very low latency and ability to connect millions of devices simultaneously, 5G provides the foundation of the next generation technology such as Artificial Intelligence (AI), the Internet of Things (IoT), smart cities and self-driven cars.
The topic of this paper is the development of the programs of 5G, its technical operation, its safety, and its colossal role in intelligent systems and highly advanced infrastructure. It is only logical to continue entering the digital age as far as speaking about the possibilities and the outcomes of the 5G will become inseparable elements of creating the world that would be wiser, safer, and connected.
The evolution of 5G
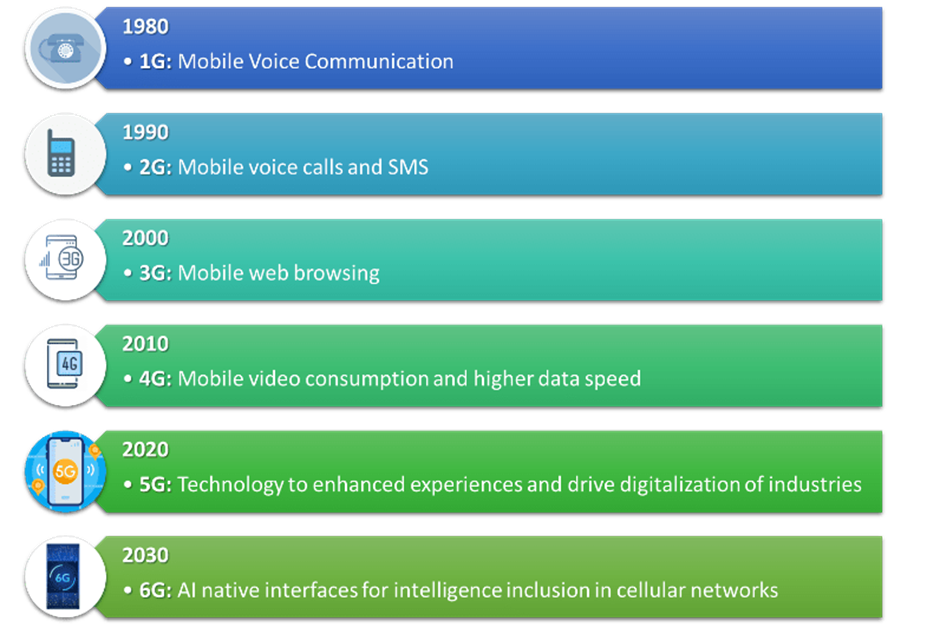
The 5G is an evolution of the mobile communication technology involving successive inches of speed, connectivity, and capabilities as was the case between 1G, 2G, 3G, and 4G. Compared to previous generations, which mainly aimed at voice and basic data transfer, 5G brings significantly higher data speeds, ultra-low latency, massive connectivity of devices, and smarter network possibilities to many industries.
The fact of the gradual evolution of generations of cells can be observed in the historical sequence of their life:
- 1G (1980s): Analog voice calling.
- 2G (1990s): Digital speech and primitive texting; data speed of 10 KB ps.
- 3G (early 2000s): 384 KBps-5Mbps with the capability of connecting to the internet and exchanging video communication through handheld machines.
- 4G (later 2000s/2008s): 200 Mbps high-speed broadband pipelines can stream HD video, play games and use more sophisticated cellular services.
The 2020s will bring with them 5G and the new technologies that enable it (millimeter waves, small cells, large arrays of multiple-input multiple-output and beamforming) to provide a new level of performance. It enables numerous applications ranging in autonomous vehicles, smart cities, and enhanced healthcare. 5G also introduces network architectures of software-based networks, AI/machine learning on network optimization and network slicing on the customized virtual networks.
This is further developed with 5G-Advanced (or 5.5G), in 3GPP Release 18, 5.5G is a 6G, wimax transitional step. Its features will maximize spectral efficiency and energy efficiency, widen the capability on massive machine-type communication, ultra-low latency critical services, and facilitate supporting the extended reality (XR). It incorporates AI/ML to make network operations smarter and handover reliability as well as such new features as geolocation that is independent of the satellite system. There are demonstrations of the 5G-Advanced exceeding 10 Gbps, and these will be in deployment in 2025.
Functioning of the 5G
The fifth-generation mobile communication technology, also known in short as 5G, is a major progression in the wireless network offering great advantages in terms of absolute velocity, absolute dependability, and a decrease in latency. This system possesses a cell structure with the geographically large territories being disintegrated into small areas called cells. In and among these cells, they have provided the means of communication using encoded radio signals relayed through radio waves thereby promising contest in coverage and connectivity.
The higher frequency bands are one of the characteristics of 5G and which is used below and above 6GHz. Such frequencies enable speeds in data transmission that is higher, hence making download and upload speeds much faster than those supported by fourth generation (4G) networks. This capability is increasingly necessary to help data-intensive processes, including high-definition video streaming, cloud gaming, and immersive virtual reality environments.
The bulk of the 5G deployed to date remains a non-standalone network and has not yet moved to its own core operations. However, with the increasing number of dedicated infrastructures, 5G would probably develop into fully independent systems that would offer the greatest amount of performance, efficiency and scalability.
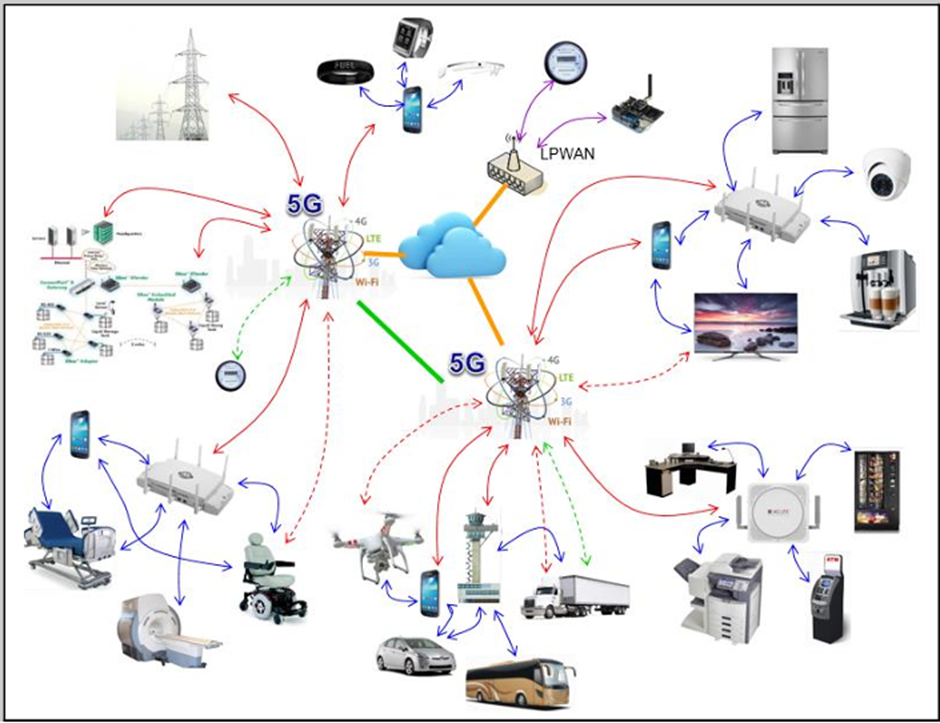
One of the outstanding attributes of 5G is the age of multi-access edge computing (MEC). MEC enables data to be computed at the network edge as opposed to concentrated servers, which extensively lessens latency. This responsiveness is a key enabler of the emerging new technologies and applications, including the Internet of Things (IoT), smart transportation and autonomous transport, telemedicine and smart city projects
Impact of 5G
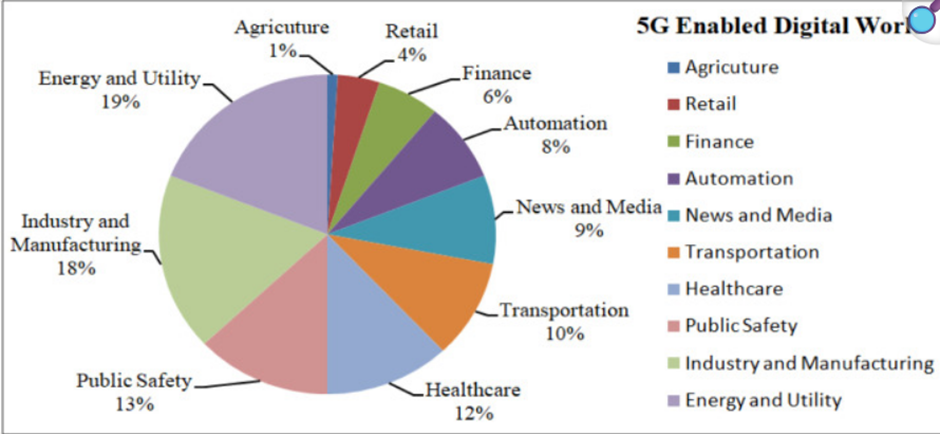
5G technology is transforming society and industries. In smart cities, 5G can be applied to enable connections to massive IoT and are applied in supporting real-time data on millions of sensors to encompass smart energy management, security in the city, and efficient transportation services. This will automate the livability and sustainability of the cities with the use of smart infrastructure.
In health care, 5G will have effective telemedicine, remote monitoring and even robotic surgery due to ultra-reliable low latency. It also involves AR (Augment Reality) and VR (Virtual reality ) medical training and diagnostics. 5G has proved to be helpful in education; it has facilitated online training by means of immersive learning and availability of virtual learning contents in far off areas. 5G can be useful in the transportation sector to facilitate intelligent traffic management, autonomous vehicle development and solve safety and efficiency in mass urban transportation. In financial terms, 5G will play a central role in Industry 4.0 and amplify production through automation and intelligent maintenance and innovation and new forms of business. By the year 2030, 5G is expected to have an impact on the global GDP to the tune of a cumulative 11 trillion and resultantly create masses of job opportunities and broad economic application in various sectors which include manufacturing, financial as well as the delivery of public services.

The future of smart innovation with 5G
The real potential of smart innovation with 5G and beyond lies in the ability to integrate some of the new emerging technologies like AI, AR/VR and autonomous systems. 5G super-fast speeds and super low latency allow real-time immersive Ness with AR and VR, which has valuable applications in virtual training, real-time collaboration, interactive e-commerce, and high-resolution simulations. AI can make these settings even more immersive by adjusting the experience to better communicate through natural language and computer vision and adjust the visuals as they move through the setting. The combination of 5G, AI, AR/VR opens exciting opportunities to develop new approaches and the greatest use-user experience in industry and work in healthcare, education, manufacture, and retail.
The autonomous networks also have access to the secure high-bandwidth connections that 5G provides so that vehicles, drones and robots can be directed to even greater precision and with greater safety, ensuring that programs of Industry 4.0 industrial automation and smart cities can progress at an even faster pace.
The 5G innovation is tipping more in the direction of sustainability. The 5G has contributed to the reduction of environmental pollution and climate ambitions through optimizing energy sources, increasing the resources aimed at smarter resource management, facilitating a smart grid and precision agriculture. With 5G driven OT devices, one must be able to gather data-driven insights to monitor and manage emissions, use of water as well as waste management.
6G remains a theoretical prospect, due to be introduced in about 2030, with potentially higher speeds, even lower latency, greater AI capability and universality of connectivity. 6G will be geared to redefine holographic communications, tactile internet, and fully autonomous systems, into the next digital revolution going beyond what is now available.
