Edge Computing: The Future of Computing
Edge Computing: The Future of Computing
Formerly a new technology trend to watch, cloud computing has become mainstream, dominating the market. However, as the quantity of data organizations are dealing with continues to increase, it has become clear that cloud computing has its limitations. This is where edge computing comes in.
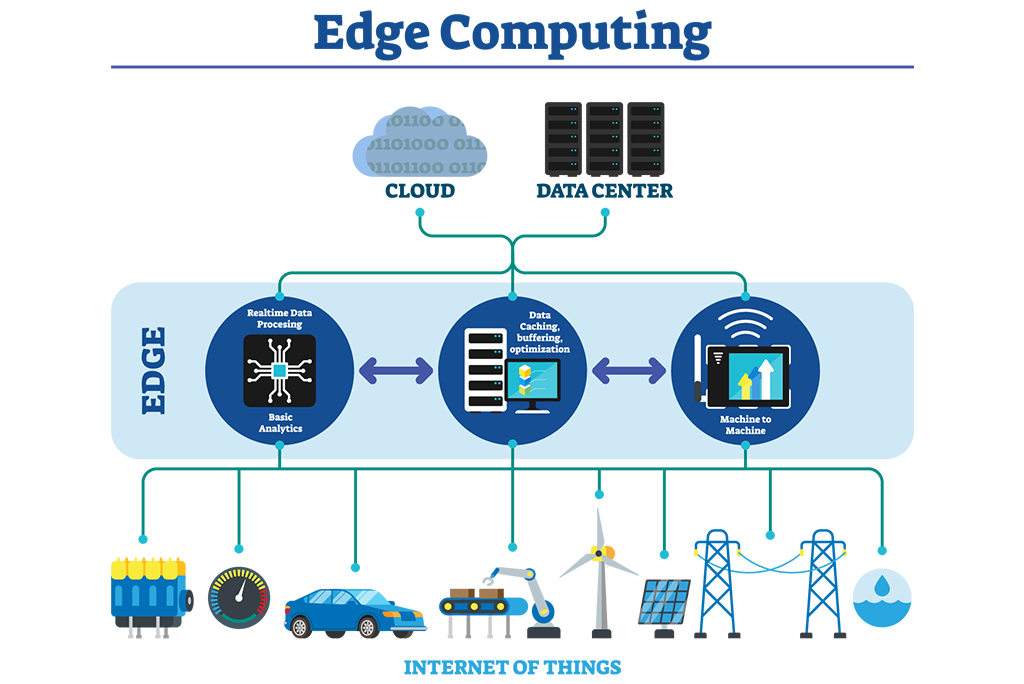
Edge computing is a distributed computing model that allows processing power to be located closer to the data source. By doing so, it reduces the latency caused by cloud computing and bypasses the need to transmit data to a central data center. This is especially useful when processing time-sensitive data in remote locations with limited or no connectivity to a centralized location.
For example, self-driving cars require instant responses to real-time data. Edge computing can help process the data from the car’s sensors in real-time, reducing the risk of accidents caused by latency. In another scenario, edge computing can be used to process data from IoT devices located in remote locations, such as oil rigs or wind turbines.
Edge computing is expected to play a vital role in the future of computing as the use of IoT devices increases. By 2023, the global edge computing market is expected to reach $6.72 billion, and this trend is only expected to grow. This growth will create various job opportunities, primarily for software engineers, making it a promising career path for those interested in technology.
In conclusion, edge computing is the future of computing, offering solutions to some of the shortcomings of cloud computing. Its ability to process time-sensitive data in remote locations with limited or no connectivity to a centralized location makes it a valuable asset in the technology industry. With the growth of IoT devices, the demand for edge computing is only set to increase, making it an exciting time for those interested in technology and innovation.
